Walls and gates
class Solution:
def wallsAndGates(self, rooms: List[List[int]]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify rooms in-place instead.
"""
INF = 2147483647
visited = []
def bfs(grid, start):
q = [start]
count = 0
while q:
size = len(q)
count += 1
for i in range(size):
x, y = q.pop(0)
visited.append((x, y))
for dx, dy in [(1, 0), (0, 1), (-1, 0), (0, -1)]:
newx = x + dx
newy = y + dy
if 0 <= newx < len(grid) and 0 <= newy < len(grid[0]):
if count < grid[newx][newy]:
grid[newx][newy] = count
q.append((newx, newy))
for i in range(len(rooms)):
for j in range(len(rooms[0])):
if rooms[i][j] == 0:
bfs(rooms, (i, j))
Walls and Gates
You are given an m x n grid rooms initialized with these three possible values.
-1A wall or an obstacle.0A gate.INFInfinity means an empty room. We use the value231 - 1 = 2147483647to representINFas you may assume that the distance to a gate is less than2147483647.
Fill each empty room with the distance to its nearest gate. If it is impossible to reach a gate, it should be filled with INF.
Example 1:
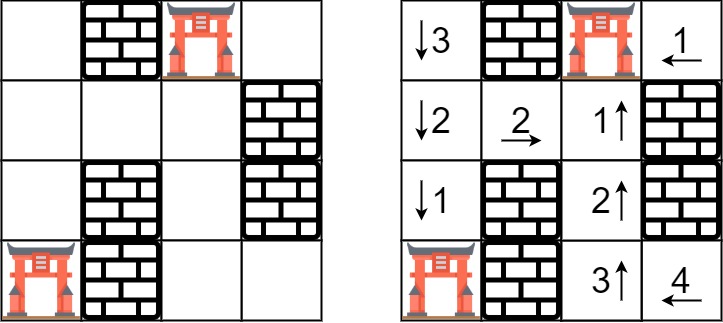
Input: rooms = [[2147483647,-1,0,2147483647],[2147483647,2147483647,2147483647,-1],[2147483647,-1,2147483647,-1],[0,-1,2147483647,2147483647]] Output: [[3,-1,0,1],[2,2,1,-1],[1,-1,2,-1],[0,-1,3,4]]
Example 2:
Input: rooms = [[-1]] Output: [[-1]]
Constraints:
m == rooms.lengthn == rooms[i].length1 <= m, n <= 250rooms[i][j]is-1,0, or231 - 1.
