Trim a binary search tree
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def trimBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], low: int, high: int) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if not root:
return None
if root.val < low:
right = self.trimBST(root.right, low, high)
return right
if root.val > high:
left = self.trimBST(root.left, low, high)
return left
root.left = self.trimBST(root.left, low, high)
root.right = self.trimBST(root.right, low, high)
return root
Trim a Binary Search Tree
Given the root of a binary search tree and the lowest and highest boundaries as low and high, trim the tree so that all its elements lies in [low, high]. Trimming the tree should not change the relative structure of the elements that will remain in the tree (i.e., any node's descendant should remain a descendant). It can be proven that there is a unique answer.
Return the root of the trimmed binary search tree. Note that the root may change depending on the given bounds.
Example 1:
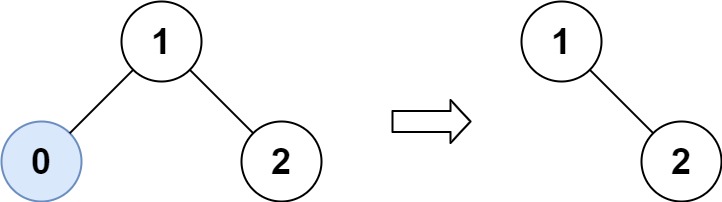
Input: root = [1,0,2], low = 1, high = 2 Output: [1,null,2]
Example 2:
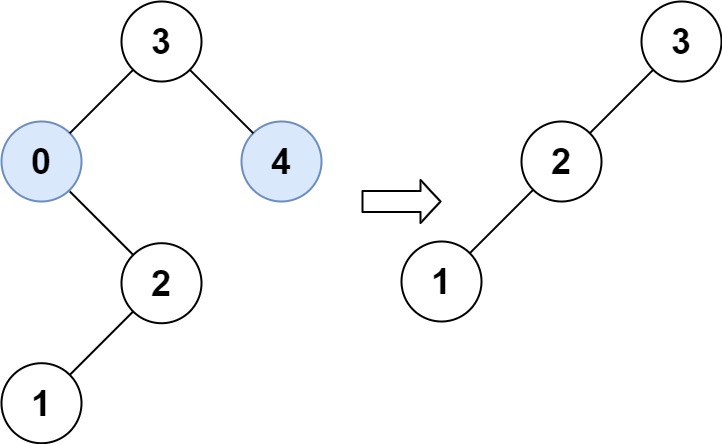
Input: root = [3,0,4,null,2,null,null,1], low = 1, high = 3 Output: [3,2,null,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. 0 <= Node.val <= 104- The value of each node in the tree is unique.
rootis guaranteed to be a valid binary search tree.0 <= low <= high <= 104
